Global Electric Traction Motor Market Size and Share
Global Electric Traction Motor Market Analysis by Mordor Intelligence
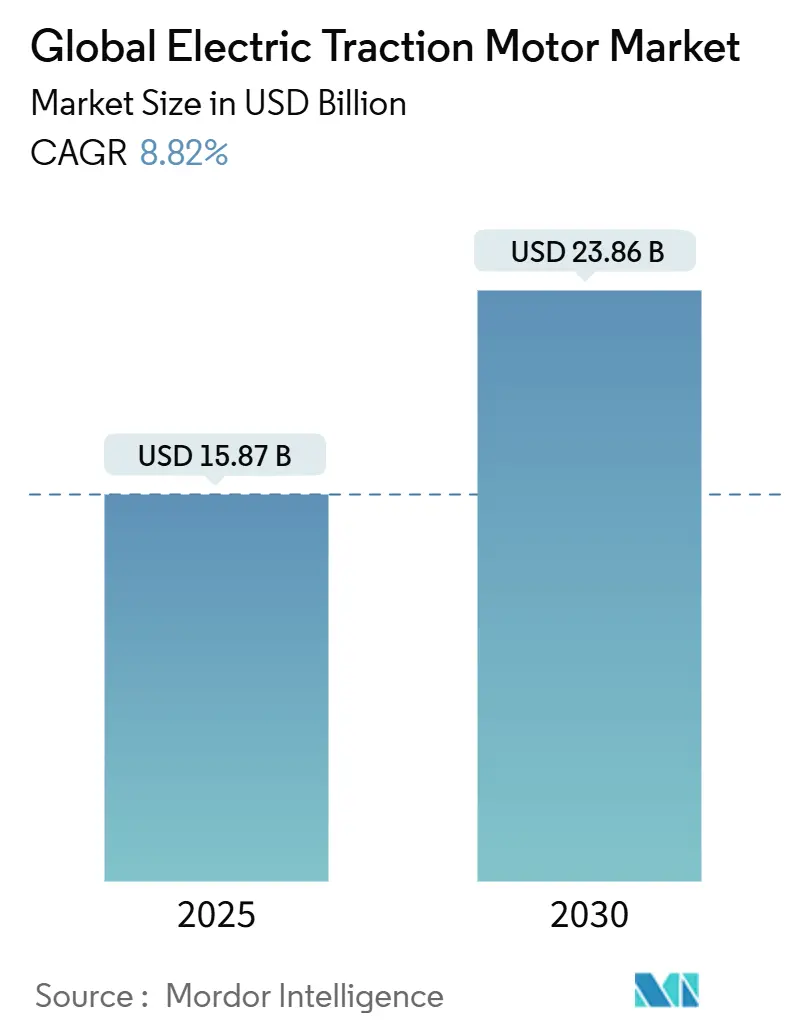
The Global Electric Traction Motor Market size is estimated at USD 15.87 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 23.86 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 8.82% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Growth is propelled by parallel advances in high-speed rail, the shift to 800 V vehicle architectures and localization policies that are redrawing global supply chains. Permanent-magnet traction motors now headline procurement for the CR450 train in China, underscoring how rail projects stimulate orders for compact, high-power machines.[1]Xinhua News Agency, “China’s CR450 Sets New Benchmark for High-Speed Rail,” news.cn In automotive, premium brands that have standardised on 800 V platforms are demanding lighter motors matched with silicon-carbide (SiC) inverters for faster charging cycles, while recycling mandates in Europe and India push regional production of critical motor components. Supply-chain resilience has become a strategic differentiator as manufacturers respond to China’s 2025 rare-earth export restrictions.[2]Center for Strategic & International Studies, “China’s Rare Earths Trade Restrictions and the Global Response,” csis.org
Key Report Takeaways
- By type, alternating-current (AC) motors led with 65% of electric traction motor market share in 2024; the same category is expanding at a 12% CAGR to 2030.
- By application, railway traction accounted for a 45% share of the electric traction motor market size in 2024, whereas electric vehicles are projected to grow the fastest at 16% CAGR through 2030.
- By power rating, motors below 200 kW held 55% of the electric traction motor market size in 2024, while the 200-400 kW band is forecast to post a 10% CAGR to 2030.
- By cooling method, air-cooled units commanded 60% share in 2024; liquid-cooled designs are registering the quickest growth at 11.5% CAGR.
- By voltage class, 1-3 kV systems represented 50% of electric traction motor market share in 2024, yet sub-1 kV systems tied to 800 V vehicles are rising at 10.5% CAGR.
- By region, Asia-Pacific captured 50% of the electric traction motor market share in 2024, and is also the fastest-growing geography with a 10% CAGR through 2030.
Global Electric Traction Motor Market Trends and Insights
Drivers Impact Analysis
| Driver | (~) % Impact on CAGR Forecast | Geographic Relevance | Impact Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surge in high-speed rail electrification projects across Asia | +2.1% | Asia-Pacific core, spill-over to North America | Medium term (2-4 years) |
| OEM shift toward in-house e-axle integration using 800 V traction motors in premium EVs | +1.8% | Global, concentrated in Europe & China | Short term (≤ 2 years) |
| Adoption of SiC inverters enabling higher-frequency motors below 70 kg | +1.4% | North America & EU, expanding to APAC | Medium term (2-4 years) |
| Government-backed localisation mandates for motor manufacturing in India and EU CBAM | +1.2% | India, EU, secondary effects in Southeast Asia | Long term (≥ 4 years) |
Source: Mordor Intelligence
Surge in High-Speed Rail Electrification Projects Across Asia
China’s CR450 programme, Turkey’s Eastern Middle Corridor and the federally backed California line each call for lightweight, high-speed rolling stock powered by permanent-magnet motors. The California corridor alone secured USD 3.1 billion in federal funds to source 220 mph trainsets fitted with 200-400 kW motors that maximise power-to-weight ratios.[3]California High-Speed Rail Authority, “Federal Government Awards USD 3.1 Billion for California High-Speed Rail,” hsr.ca.gov High-speed rail demand spills into auxiliary equipment—substations, cooling blowers and door actuators—adding secondary pull for fractional-horsepower machines. Inter-regional technology cooperation is also evident, with Japanese suppliers exporting vibration-tested inverter units designed for 20 kHz switching frequencies. As Asia continues to link megacities with 350 km/h corridors, long-term maintenance contracts lock in recurring motor sales over a 30-year rolling stock lifespan. Rail packages often bundle energy-recovery braking modules, broadening revenue opportunities for specialist motor house
OEM Shift Toward In-House e-Axle Integration Using 800 V Traction Motors in Premium EVs
Volkswagen, Mercedes-Benz and Hyundai have moved final e-axle assembly inside their own plants to gain tighter control over software-defined torque management and thermal envelopes. Magna’s new 800 V e-drive built in Tamil Nadu typifies the regionalisation trend, while BorgWarner’s HVH 320 motor targets 300 kW commercial vans that need sub-20-minute fast-charging. In-house architectures can integrate SiC inverters on the same coolant loop, eliminating duplicated pumps and trimming harness weight by 15%. The optimisation delivers up to 20% efficiency improvement in WLTP cycles, translating into smaller battery packs for equivalent range. Tier-1 suppliers with mixed semiconductor-mechanical portfolios are advantaged because torque curves now depend more on gate-driver tuning than on lamination tweaks. The strategy has triggered a component realignment, with winding-line vendors shifting capacity from six-phase induction formats to hair-pin permanent-magnet stators.
Adoption of Silicon-Carbide (SiC) Inverters Enabling Higher-Frequency Motors Below 70 kg
SiC devices cut switching losses by as much as 70%, letting designers raise fundamental electrical frequency above 20 kHz without excessive heat. Infineon has committed EUR 5 billion for 200 mm SiC wafer capacity in Kulim and Dresden to secure supply for mobility clients. Higher frequencies shrink the magnetic core, which is why Evolito’s liquid-cooled axial-flux unit hits 150 kW at only 27 kg, an attractive metric for eVTOL airframes. Automotive tests show that pairing SiC inverters with hair-pin windings lifts peak system efficiency beyond 95%, trimming drive-cycle losses equivalent to 50 kg of battery mass. Weight-sensitive sectors such as light-delivery drones and intralogistics fleets are early adopters because payload capacity directly converts to revenue. Falling SiC substrate prices are projected to trigger a mid-decade inflection where 400 V mid-range passenger vehicles also switch from silicon IGBTs to SiC MOSFETs.
Government-Backed Localisation Mandates for Motor Manufacturing in India and EU CBAM
India’s Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme earmarks INR 25,938 crore (USD 3.1 billion) to encourage domestic traction-motor lines and ties the subsidies to a minimum localisation threshold of 50%. Parallel European rules under the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism levy import carbon costs, making offshore magnet pressing less attractive. ABB reacted by reserving INR 1,000 crore for a campus at Peenya that doubles switchgear and motor output. Local content rules de-risk rare-earth shortages while building a knowledge base in rotor-balancing, vacuum pressure impregnation and precision-machining. Policymakers believe co-locating battery and motor gigafactories will accelerate a virtuous cycle of lower logistics cost, faster engineering change and improved energy security.
Restraints Impact Analysis
| Restraint | (~) % Impact on CAGR Forecast | Geographic Relevance | Impact Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Limited rare-earth recycling infrastructure constraining permanent-magnet motor supply in Europe | -1.30% | Europe, secondary effects in North America | Medium term (2-4 years) |
| Thermal management challenges above 400 kW in compact EV platforms | -0.80% | Global, acute in premium EV segment | Short term (≤ 2 years) |
Source: Mordor Intelligence
Limited Rare-Earth Recycling Infrastructure Constraining Permanent-Magnet Motor Supply in Europe
Europe currently imports more than 90% of its rare-earth supply, with China controlling the bulk of refining capacity, leaving rail and automotive OEMs exposed to geopolitical shocks. Existing EU recycling can satisfy only 8-19% of magnet demand by 2030, and even in a high-collection scenario the rate tops out at 48% in 2050, pointing to a structural shortfall. Regulatory gaps, such as inconsistent end-of-life labelling and limited financial incentives, hamper investment in shredding, separation and hydrometallurgy lines. WSP’s Belfast study confirmed economic viability for a 3,600-tonne-per-year oxide refinery yet warned that feedstock certainty is critical for bankability. European policy makers are now debating mandatory magnet take-back schemes to raise collection rates, though opposition from small-volume motor assemblers could delay adoption. Until recycling scales up, train builders like Alstom hedge supply by dual-sourcing induction motors and stockpiling critical alloys.
Thermal Management Challenges Above 400 kW in Compact EV Platforms
In super-sport utility and haulage segments, sustained power above 400 kW quickly leads to hotspot formation in windings and stator teeth, risking partial demagnetisation or insulation failure. Liquid cooling resolves part of the issue but adds up to 40 kg in pumps, manifolds and glycol lines, diluting energy-density gains. 800 V systems exacerbate the hurdle because thicker insulation and greater creepage distances are required to meet IEC 60664 standards. SiC inverters cut switching loss but the motor core still contends with I²R and iron-loss heating, forcing derating under high ambient temperatures. Some truck OEMs now parallel two mid-power motors in an e-tandem axle rather than scale a single unit, spreading heat sources and easing packaging. Research is converging on next-generation stator resins and integrated micro-channel cooling plates, but commercialisation timelines extend into the next decade.
Segment Analysis
By Type: AC Motors Dominate Through Efficiency Advantages
The electric traction motor market size attributed to AC designs was USD 9.42 billion in 2024, equal to 65% of total value, and this category is projected to expand at a double-digit pace through 2030. Permanent-magnet synchronous units underpin the trajectory because they deliver high torque density, critical for weight-sensitive passenger cars and high-speed rail cars. Japanese policy, channelled via METI, earmarks subsidies for hair-pin winding automation, reinforcing the domestic ecosystem for low-loss AC machines. Induction motors continue to equip locomotives that value ruggedness over ultimate efficiency, while switched-reluctance offerings gain share in low-cost city buses that tolerate greater torque ripple.
The DC segment remains relevant in specialised niches such as automated guided vehicles and drone propulsion where controller simplicity and low base cost matter more than peak efficiency. Brushless DC variants outperform brushed equivalents in reliability but face competition from miniature PM AC motors as SiC inverter prices fall. Overall, AC dominance is secure because inverter sophistication and magnet pricing trends favour high-efficiency use-cases. Motor makers consequently invest in ferrite-assisted synchronous topologies to mitigate rare-earth risk, especially for mid-range vans.
By Power Rating: Mid-Range Segment Accelerates Commercial Vehicle Adoption
Motors under 200 kW generated 55% of the electric traction motor market size, equating to USD 7.97 billion in 2024, mostly serving passenger EVs, light rail and last-mile logistics vehicles. However, the 200-400 kW band is forecast to record the fastest 10% CAGR as medium-duty trucks, intercity buses and 220 mph trainsets require higher continuous output. This range balances torque demand with manageable thermal loads, avoiding the complexity of dual loop liquid systems necessary above 400 kW.
Above 400 kW machines power heavy freight locomotives and large industrial drives yet post slower growth because of thermal ceilings in compact chassis. Siemens Mobility’s Vectron Dual Mode locomotive illustrates how system engineers combine diesel and 2.4 MW electric modules to navigate partially electrified routes.[4]Siemens AG, “Akiem Orders 50 Vectron Dual Mode Locomotives from Siemens Mobility,” press.siemens.com Designers examining axial-flux architectures hope to compress high-power units for marine thrusters and air-taxis, but winding end-turn cooling remains a gating factor. Consequently, multiple smaller motors arranged in distributed drives are replacing single monolithic units in heavy trucks.

Note: Segment share of all individual segment available on report purchase
By Cooling Type: Liquid Systems Gain Ground Despite Air-Cooled Dominance
Air-cooled motors retained a 60% revenue share in 2024 because they meet most passenger-car duty cycles and are cheaper to assemble. Yet liquid-cooled alternatives are expanding at an 11.5% CAGR as development programmes push power density higher, especially in trucks, eVTOL aircraft and premium sedans. Ducted oil-spray cooling lets manufacturers raise peak current without enlarging the stator, a clear benefit for skateboard EV platforms.
Industry leaders package shared coolant loops that feed motor, inverter and battery, cutting system parts count while easing homologation. Evolito’s 150 kW axial-flux motor for Flying Whales improved continuous torque by 30% thanks to direct rotor-core coolant passages. Air-over models remain optimal for metro rail fans and screw compressors where space is abundant, but product-roadmap signals point to wider adoption of integrated liquid plates, especially once seal reliability crosses aviation thresholds.
By Voltage Class: Low-Voltage Segment Accelerates With Automotive Adoption
Systems operating below 1 kV represented the quickest-growing slice, advancing at 10.5% CAGR as vehicle platforms converge on 800 V batteries to cut charge time to sub-18 minutes. In contrast, the 1-3 kV class, dominant in railway traction, led the electric traction motor market share at 50% and generated USD 7.24 billion in 2024. The European Commission’s Technical Specifications for Interoperability standardise 25 kV overhead power but still rely on 3 kV DC at the onboard converter, keeping that voltage window firmly entrenched.[5]European Commission, “Technical Specifications for Interoperability: Energy Sub-System,” ec.europa.eu
Below-1 kV designs leverage insulated-gate drivers rated at 1,200 V, ensuring headroom over 800 V batteries while cutting conductor cross-section by 20%. Cable weight savings translate into noticeable range gains for cross-over utility vehicles. Above 3 kV systems continue to serve niche pipelines such as mining locomotives and drilling rigs, though insulation cost and certification hurdles contain growth to single-digit rates.

Note: Segment share of all individual segment available on report purchase
By Application: Electric Vehicles Disrupt Railway Dominance
Railway traction held a 45% stake in 2024, thanks to longstanding electrification in Europe, China and Japan. Nonetheless, electric vehicle demand is racing ahead with a 16% CAGR that will make automotive the primary volume contributor by 2030. China delivered 6.9 million EVs in 2024 and is targeting a 40% global share by the end of the decade. Scaling output lowers per-kW motor cost, inviting further adoption in two-wheelers, small vans and autonomous shuttles.
Industrial machinery remains a steady but unglamorous customer where servo-like dynamic response outweighs headline efficiency. Emerging air-taxi programmes and drone fleets represent micro-markets yet garner outsized R&D attention due to stringent size-weight-power-cost constraints. Combined, these new segments encourage experimentation in axial-flux and magnet-free reluctance topologies, broadening design diversity within the electric traction motor market.
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific contributed USD 7.25 billion to the electric traction motor market size in 2024 and is projected to grow 10% annually through 2030. China’s colossal EV manufacturing base, intertwined with domestic magnet supply and policy support, anchors regional momentum. Japan focuses on loss-reduction R&D for synchronous machines to meet carbon-neutral pledges, while India’s PLI incentives attract capital for power-train plants targeted at both export and domestic two-wheeler demand.
Europe ranked second, driven by Fit-for-55 emissions targets, the 2035 internal-combustion phase-out, and record investment in transnational rail corridors. German OEMs fast-track SiC inverters to unlock next-generation e-axles and protect high-value employment. Meanwhile, the European Commission’s CBAM framework fosters motor assembly localisation, complementing the bloc’s ambitions for self-sufficiency in strategic raw materials.
North America’s resurgence is tied to the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, which channels USD 66 billion into passenger and freight rail upgrades, plus state-level zero-emission mandates that elevate commercial EV penetration. Federal-state co-financing of battery and magnet recycling plants further cushions supply risks. South America and the Middle East & Africa, though smaller today, witness sporadic rail concessions and rising city-bus electrification programmes that set the stage for future scale once funding pipelines stabilise.

Competitive Landscape
The electric traction motor market remains moderately fragmented, yet application-specific concentration levels vary. Rail motors lean oligopolistic; ABB, Siemens and CRRC collectively control an estimated 60% of OEM deliveries, benefiting from installed-base service contracts. Automotive supply is more diffuse, as new entrants such as Nidec, Dana TM4 and several Chinese tier-1s contest legacy players on cost, software and integration know-how.
Strategic moves centre on vertical integration and regional supply-chain localisation. ABB India doubled motion-segment revenue after inaugurating a digitally enabled plant in Bengaluru, reducing lead time for traction drives by 30%. Siemens Mobility advanced its dual-mode locomotive range, securing a 50-unit order from Akiem that underscores demand for flexible traction options on partly electrified lines. Concurrently, component shortages prompted partnerships—CRRC inked MOUs with Australian miners for dysprosium supplies while Stellantis signed long-term offtake deals with MP Materials for NdFeB alloys.
Technology differentiation is narrowing as software-defined torque management and SiC inverter integration become hygiene factors rather than unique selling points. Suppliers compete on thermal design, magnet economics and lifecycle analytics enabled by onboard edge devices. Smaller firms gain traction by focusing on axial-flux or switched-reluctance niches, licensing designs to large assemblers needing quick portfolio diversification. Overall, the interplay of policy pressures, material constraints and application diversification keeps competitive intensity high.
Global Electric Traction Motor Industry Leaders
-
Siemens AG
-
CRRC Corporation Limited
-
ABB Ltd
-
Nidec Corporation
-
Toshiba Corporation
- *Disclaimer: Major Players sorted in no particular order

Recent Industry Developments
- June 2025: Siemens Mobility secured an order for 50 Vectron Dual Mode locomotives from Akiem, with an option for 40 more, spotlighting greener rail traction capable of 2.4 MW electric operation.
- April 2025: China imposed export licences on seven rare-earth elements critical for traction motors, heightening supply-chain vigilance.
- January 2025: Siemens Mobility landed EUR 670 million of infrastructure and service contracts with HS2 Ltd for Britain’s high-speed line.
- November 2024: The World Bank approved a EUR 607.4 million loan for Turkey’s Middle Corridor Railway electrification project.
Global Electric Traction Motor Market Report Scope
The electric traction motor market report includes:
| By Type | Alternating Current (Induction, Permanent-Magnet Synchronous, Switched Reluctance) | ||
| Direct Current (Brushed, Brushless DC) | |||
| By Power Rating | Below 200 kW | ||
| 200 to 400 kW | |||
| Above 400 kW | |||
| By Cooling Type | Air-Cooled | ||
| Liquid-Cooled | |||
| Self-Ventilated | |||
| By Voltage Class | Below 1 kV | ||
| 1 to 3 kV | |||
| Above 3 kV | |||
| By Application | Railway | ||
| Electric Vehicles | |||
| Industrial Machinery | |||
| Other Applications (Drones, eVTOL) | |||
| By Geography | North America | United States | |
| Canada | |||
| Mexico | |||
| Europe | Germany | ||
| France | |||
| United Kingdom | |||
| Italy | |||
| Spain | |||
| Netherlands | |||
| Rest of Europe | |||
| Asia-Pacific | China | ||
| Japan | |||
| South Korea | |||
| India | |||
| ASEAN Countries | |||
| Rest of Asia-Pacific | |||
| South America | Brazil | ||
| Argentina | |||
| Rest of South America | |||
| Middle East and Africa | Saudi Arabia | ||
| United Arab Emirates | |||
| South Africa | |||
| Egypt | |||
| Rest of Middle East and Africa | |||
| Alternating Current (Induction, Permanent-Magnet Synchronous, Switched Reluctance) |
| Direct Current (Brushed, Brushless DC) |
| Below 200 kW |
| 200 to 400 kW |
| Above 400 kW |
| Air-Cooled |
| Liquid-Cooled |
| Self-Ventilated |
| Below 1 kV |
| 1 to 3 kV |
| Above 3 kV |
| Railway |
| Electric Vehicles |
| Industrial Machinery |
| Other Applications (Drones, eVTOL) |
| North America | United States |
| Canada | |
| Mexico | |
| Europe | Germany |
| France | |
| United Kingdom | |
| Italy | |
| Spain | |
| Netherlands | |
| Rest of Europe | |
| Asia-Pacific | China |
| Japan | |
| South Korea | |
| India | |
| ASEAN Countries | |
| Rest of Asia-Pacific | |
| South America | Brazil |
| Argentina | |
| Rest of South America | |
| Middle East and Africa | Saudi Arabia |
| United Arab Emirates | |
| South Africa | |
| Egypt | |
| Rest of Middle East and Africa |
Key Questions Answered in the Report
What is the current size of the electric traction motor market?
The electric traction motor market was valued at USD 14.49 billion in 2024 and is forecast to hit USD 23.86 billion by 2030, growing at an 8.82% CAGR.
Which region leads demand for electric traction motors?
Asia-Pacific holds 50% of global demand and is also the fastest-growing region with a projected 10% CAGR through 2030, driven by China’s EV scale-up and extensive rail electrification.
How fast is the automotive application growing?
Electric vehicle demand for traction motors is expanding at a 16% CAGR, making it the quickest-growing application segment through 2030.
Why are SiC inverters important for traction motors?
Silicon-carbide inverters reduce switching losses, allow higher operating frequencies and enable lighter, more efficient motors, especially in 800 V vehicle architectures.
What are the key supply-chain risks for motor manufacturers?
Rare-earth material availability, limited European recycling capacity and new export restrictions pose near-term risks, while thermal management above 400 kW remains a technical hurdle.
Which cooling technology is gaining traction?
Liquid-cooled systems are growing at 11.5% CAGR because they support higher power densities required in commercial EVs and emerging eVTOL aircraft.



