India Drug Delivery Devices Market Analysis by Mordor Intelligence
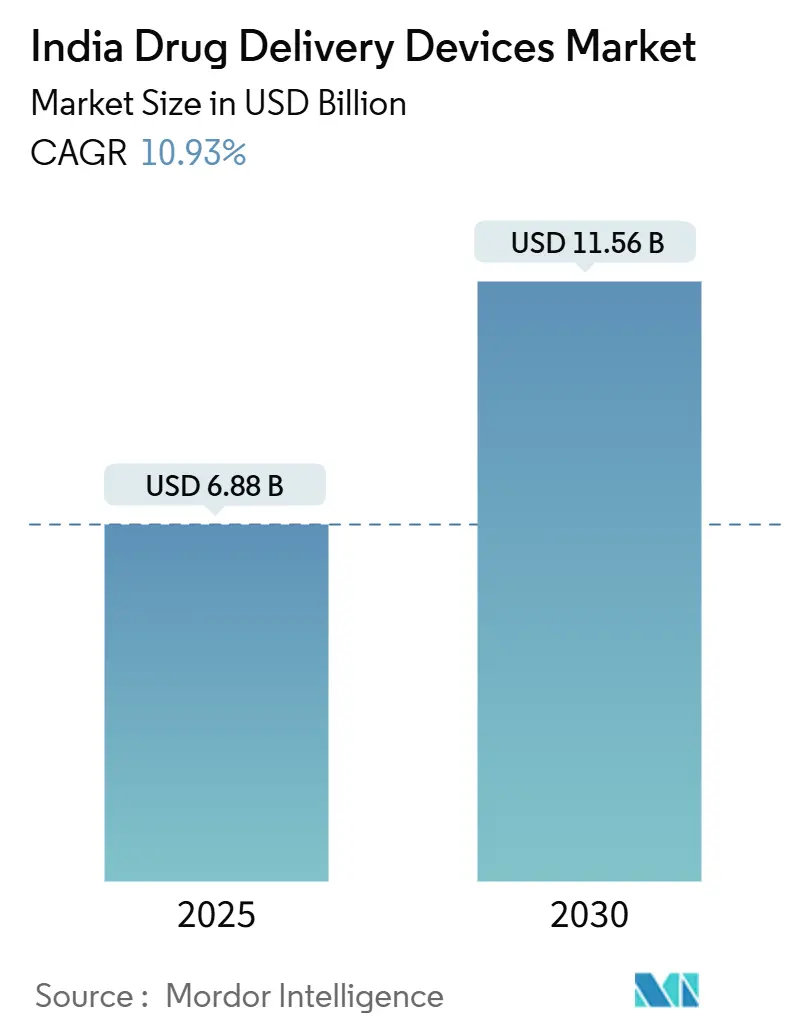
The India drug delivery devices market is valued at USD 6.88 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 11.56 billion by 2030, reflecting a 10.93% CAGR through the forecast period. Expanding healthcare infrastructure, a sharp rise in chronic disease prevalence, and policy support for domestic production are driving sustained demand for advanced therapeutic platforms. Continued government funding under the Production Linked Incentive scheme and fast-track regulatory pathways have lowered barriers for novel devices, particularly in injectables and connected systems. Manufacturers are also benefiting from the National Medical Devices Policy 2023, which aligns standards with global norms and fosters local innovation clusters in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, and Himachal Pradesh. Persistent cost pressures in India’s predominantly out-of-pocket healthcare market have pushed suppliers to develop value-oriented, user-friendly technologies that can safely transition from hospital to home settings.
Key Take Aways
- By device type, injectable delivery devices led with 45.0% revenue share in 2024; implantable systems are projected to expand at a 12.04% CAGR to 2030.
- By route of administration, injectables accounted for 50.0% share of the India drug delivery devices market size in 2024, while the nasal route is advancing at an 11.45% CAGR through 2030.
- By application, diabetes captured 32.0% of the India drug delivery devices market share in 2024 and neurological disorders are set to grow at a 12.56% CAGR to 2030.
- By end user, hospitals held 48.0% share of the India drug delivery devices market size in 2024, whereas home healthcare settings are rising at a 13.67% CAGR to 2030.
India Drug Delivery Devices Market Trends and Insights
Drivers Impact Analysis
| Driver | (~) % Impact on CAGR Forecast | Geographic Relevance | Impact Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Government Initiatives To Support Healthcare Access | 3.2% | National, with stronger impact in Tier-1 and Tier-2 cities | Medium term (2-4 years) |
| High Demand for Cost Effective Drugs Such as Biosimilar | 2.6% | National, with emphasis on urban centers | Medium term (2-4 years) |
| High Burden of Chronic and Infectious Diseases Coupled with Aging Population | 2.2% | National, with higher prevalence in urban areas | Long term (≥ 4 years) |
| Government and Market Players Initiatives for Boosting Domestic Manufacturing of Medical Devices | 2.0% | National, concentrated in manufacturing hubs like Gujarat, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu | Medium term (2-4 years) |
| Technological Advancement and Increased Awareness for Smart/Connected Drug Delivery Devices | 1.6% | Urban centers, primarily metropolitan cities | Medium term (2-4 years) |
| Rapid Expansion of Home-care & Telemedicine Models Encouraging Self-administration Devices | 1.5% | Urban and semi-urban areas, with gradual expansion to rural regions | Short term (≤ 2 years) |
Source: Mordor Intelligence
Government Initiatives To Support Healthcare Access
Public spending on health rose to INR 89,287 crore in the 2024-25 Union Budget, channeling capital into primary care and device procurement within Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.[1]Press Information Bureau, “Union Budget 2025-26 Highlights,” pib.gov.in A streamlined approval pathway under the National Medical Devices Policy 2023 now accelerates clearances for injectable and implantable systems, cutting previous timelines by nearly one-third. Coupled with the Export Promotion Council for Medical Devices established in 2025, local firms gain faster export certifications and market entry support. These policy moves have widened adoption of affordable autoinjectors in semi-urban hospitals, fueling incremental demand across the India drug delivery devices market. Increased funding further supports clinical validation studies, ensuring new domestic products meet international standards.
High Demand for Cost-Effective Drugs Such as Biosimilars
Indian biosimilar producers, led by Biocon and Dr. Reddy’s, have launched low-cost versions of biologics that require dedicated delivery formats. Biocon’s generic liraglutide received clearance in 2024, triggering higher volumes of reusable pens designed for multi-dose regimens. As 15 additional peptide formulations near approval, demand has surged for compact autoinjectors configured for subcutaneous delivery in home settings. Urban adoption is especially strong, where clinicians now prescribe biosimilars to lower total treatment expenses, thereby expanding penetration of connected pens that upload dosing data to electronic medical records. The virtuous cycle between biosimilar growth and device innovation strengthens competitiveness of domestic firms in the India drug delivery devices market.
High Burden of Chronic and Infectious Diseases Coupled with Aging Population
India reported 101 million adults living with diabetes in 2024, driving widespread use of smart pens and wearable insulin pumps that fine-tune doses and track adherence. Parallel growth in neurological disorders—projected to affect 30 million people by 2030—has intensified interest in implantable pumps capable of bypassing the blood–brain barrier.[2]Frontiers in Medicine, “Advances in Drug Delivery Systems for Neurological Disorders,” frontiersin.org These demographic pressures have prompted hospitals to standardize patient education around self-administration devices, while payers explore outcome-based reimbursement for connected therapies. Sustained-release technologies embedded with sensors now allow clinicians to tailor regimens for patients managing multiple chronic conditions, reinforcing demand across the India drug delivery devices market.
Government and Market Players Initiatives for Boosting Domestic Manufacturing of Medical Devices
PLI scheme funding rose to INR 2,444.93 crore in 2025-26 and has attracted investments worth INR 1.46 lakh crore across medical devices.[3]Department of Pharmaceuticals, “Production Linked Incentive Scheme Overview,” pharma-dept.gov.in State-level programs, such as Haryana’s Medical Devices Manufacturing Policy 2024, add fiscal incentives like capital subsidies and SGST reimbursement to stimulate plant construction.[4]Invest Haryana, “Medical Devices Manufacturing Policy 2024,” investharyana.in Newly operational device parks now support precision moulding and clean-room facilities, critical for implantable reservoirs and smart inhaler components. Strategic equity moves, including TPG’s USD 300 million investment for 35% of SCHOTT Poonawalla, reinforce supply chains for prefillable syringes. Combined policy and private capital reduce import dependence and enhance the competitive edge of the India drug delivery devices market in global tenders.
Restraint Impact Analysis
| Restraint | (~) % Impact on CAGR Forecast | Geographic Relevance | Impact Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Out-of-Pocket Spending Restricting Adoption of Advanced Implantable Systems | -1.4% | National, with greater impact in rural and semi-urban areas | Medium term (2-4 years) |
| Regulatory Uncertainty Around Classification of Combination Products Causing Approval Delays | -1.2% | National, affecting all manufacturing and import channels | Short term (≤ 2 years) |
| Skilled Healthcare Professional Shortage in Tier-2/3 Cities Impeding Safe Use of Infusion Pumps | -1.0% | Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities, rural areas | Medium term (2-4 years) |
| Fragmented Cold-chain Logistics Limiting Reach of Temperature-Sensitive Injectable Devices | -0.8% | Rural and remote areas, with some impact in Tier-2 cities | Short term (≤ 2 years) |
Source: Mordor Intelligence
High Out-of-Pocket Spending Restricting Adoption of Advanced Implantable Systems
Out-of-pocket payments still make up 55% of India’s total health expenditure, limiting access to implantable pumps that cost USD 2,000-5,000 each. Reimbursement remains patchy outside large private insurers, pushing many patients toward lower-cost external pumps or conventional syringes. Uptake therefore concentrates in metro hospitals, creating uneven distribution across the India drug delivery devices market. Government plans to expand Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana coverage to implantable drug platforms could ease this constraint, yet short-term adoption remains capped by affordability gaps in rural districts.
Regulatory Uncertainty Around Classification of Combination Products Causing Approval Delays
The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization continues to refine rules for products that merge pharmacologic payloads with device hardware. Current dual-track review adds 8-14 months to launch timelines, delaying market entry for drug-eluting implants and nanocarrier systems. Although CDSCO joined the International Medical Device Regulators Forum in 2024, lack of harmonized guidelines complicates planning for both domestic startups and multinational firms. Stakeholders are advocating for a single-window portal to streamline dossier review and shrink time-to-clinic, a change that would remove a significant drag on the India drug delivery devices market.
Segment Analysis
By Device Type: Injectable Dominance Coupled with Implantable Momentum
Injectable delivery devices represented 45.0% of the India drug delivery devices market in 2024, reflecting high demand for pens, autoinjectors, and safety syringes across diabetes, oncology, and immunology care. Prefilled syringes minimize handling errors, while spring-loaded autoinjectors improve self-administration, particularly for aging patients who face dexterity challenges. Growing acceptance of biosimilars has expanded volume requirements for low-dead-space syringe formats and reusable pen platforms. Hospitals remain the largest customers, yet pharmacies increasingly dispense self-use devices, spurring retail distribution models.
Implantable devices are on track for a 12.04% CAGR to 2030. Materials such as titanium alloys and bioresorbable polymers provide controlled release for analgesics, antispasmodics, and neuroactive compounds. Deep-brain pumps demonstrate promise for Parkinson’s and epilepsy, with early clinical data showing sustained symptom control and lower systemic exposure. Domestic startups collaborate with IITs to refine miniaturized energy sources, aligning with Make-in-India objectives. As procurement costs fall, implantables will capture higher revenue share within the broader India drug delivery devices market size projections.

Note: Segment shares of all individual segments available upon report purchase
By Route of Administration: Injectable Leadership with Nasal Acceleration
The injectable route held a 50.0% share of the India drug delivery devices market size in 2024, supported by biologicals that cannot be delivered orally. Smart pens store dosing logs, forwarding encrypted records to clinicians, and enable early detection of non-adherence. Cold-chain innovations, such as phase-change packaging, safeguard product integrity during last-mile delivery, widening geographic reach.
Nasal delivery is moving at an 11.45% CAGR through 2030. Mucoadhesive gels and surfactant-enhanced sprays improve drug absorption and can traverse the olfactory epithelium to reach the brain. Focus areas include migraine, Alzheimer’s, and even needle-free vaccine boosters. Indian firms license membrane-permeation enhancers, shortening development cycles. Pilot programs in tertiary hospitals show strong patient preference for nasal therapies, likely to boost future India drug delivery devices market share in central nervous system indications.
By Application: Diabetes Leadership with Neurological Expansion
Diabetes accounted for 32.0% of India drug delivery devices market share in 2024. Wide availability of sub-USD 20 insulin pens and sensor-linked pumps supports daily management. Launch of inhalable insulin further diversifies non-injectable options and caters to needle-averse populations. Artificial intelligence modules now pair with continuous glucose monitors to automate basal dose titration, raising control accuracy.
Neurological disorders are poised for a 12.56% CAGR to 2030. Lipid-nano-caged molecules and polymeric wafers deliver anticonvulsants and neuroprotective agents directly to targeted structures. Clinical adoption benefits from early signals of improved cognitive outcomes in mild Alzheimer’s cohorts. Government grants encourage translational research that could enable scalable manufacture of brain-targeted implants, reinforcing growth prospects across the India drug delivery devices market.

Note: Segment shares of all individual segments available upon report purchase
By End User: Hospital Supremacy with Home Healthcare Upsurge
Hospitals secured 48.0% of India drug delivery devices market size in 2024 due to their capability to initiate therapies that require complex setup, such as synchronized infusion for oncology regimens. Central sterile supply departments have adopted RFID-tagged consumables to manage inventory of specialty syringes and pumps, reducing wastage. Continuing education programs foster in-house expertise for calibration and troubleshooting of implantable systems.
Home healthcare is growing at 13.67% CAGR as insurers and providers embrace remote monitoring. Bluetooth-enabled autoinjectors transmit real-time adherence metrics, while virtual care platforms guide dosing. Rural rollouts leverage India’s expanding 4G network to connect patients with district-level specialists. Device makers now integrate multi-language audiovisual instructions, addressing literacy variations and supporting equitable adoption across the India drug delivery devices market.

Note: Segment shares of all individual segments available upon report purchase
Geography Analysis
Metropolitan clusters—Mumbai, Delhi, and Bangalore—currently generate major revenue. Specialized hospitals located in these cities introduce high-value implantables and digital inhalers first, then cascade them to regional centers once pricing thresholds fall. Their dense insurance coverage accelerates reimbursements for premium devices, thereby sustaining cash flow for suppliers that serve the India drug delivery devices market.
Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities are the fastest-growing segments with annual expansion of roughly 15-18%. State initiatives, such as Karnataka’s specialty center upgrades, equip district hospitals with negative-pressure clean rooms suitable for sterile compounding. Telangana’s telehealth integration embeds drug-delivery data into statewide e-health repositories, enhancing clinical oversight. Jan Aushadi Kendras, now numbering over 15,000, also streamline last-mile distribution for cost-effective pens and syringes pib.gov.in. These channels distribute locally produced consumables that benefit from PLI subsidies, boosting visibility of domestic brands in the India drug delivery devices market.
Rural territories remain underpenetrated but represent significant latent demand since they house around 65% of India’s population. Challenges span affordability, device literacy, and limited cold-chain logistics. Solar-powered refrigeration units and ruggedized carrying cases now feature in pilot programs, enabling stable insulin storage in high-temperature regions. Community health workers receive tablet-based training modules on smart inhaler usage, fostering grassroots competence. As public infrastructure and micro-insurance schemes expand, rural adoption will be a decisive contributor to long-term India drug delivery devices market growth.
Competitive Landscape
Global corporations such as Medtronic, Becton Dickinson, and Baxter maintain broad portfolios that span infusion, implantables, and safety syringes. Domestic leaders—Cipla, Sun Pharmaceutical, Biocon—leveraged biosimilar success to diversify into companion pens and nebulizers. The Production Linked Incentive scheme attracts collaborations where foreign original-equipment manufacturers license tooling to Indian partners, trimming import tariffs and meeting value-addition norms. TPG’s stake in SCHOTT Poonawalla augments local glass cartridge production that feeds multiple autoinjector programs.
Emerging startups exploit software strengths to create sensor-rich platforms. Bengaluru’s InsuLoop integrates closed-loop algorithms that adjust basal insulin flow based on real-time glycemic data, while Pune-based RespiraTech engineers 3D-printed inhalers with QR-code coaching overlays. These firms differentiate through aftermarket ecosystems that bind users to cloud analytics dashboards, raising switching costs and shaping purchasing decisions across the India drug delivery devices market.
White-space opportunities lie in mid-tier pricing for wearable injectors. Current import substitutes cost USD 350-400 per unit, limiting acceptance in value-sensitive segments. Local contract manufacturers can reduce cost by 25-30% by leveraging proximity to polymer suppliers and low-cost assembly labor. Likewise, the biosimilar delivery niche remains contested as innovators hurry to bundle device exclusivity with drug filings ahead of 2030 patent cliffs. Competitive intensity will likely elevate research alliances, tech-licensing agreements, and cross-border joint ventures, nudging the India drug delivery devices market toward higher consolidation over time.
India Drug Delivery Devices Industry Leaders
-
Medtronic Plc
-
Cipla Ltd
-
Becton, Dickinson and Company
-
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
-
Novo Nordisk India Pvt Ltd
-
Medtronic Plc
- *Disclaimer: Major Players sorted in no particular order

Recent Industry Developments
- May 2025: TPG acquired a 35% stake in SCHOTT Poonawalla for USD 300 million, enhancing the domestic supply of glass cartridges and prefillable syringes.
- March 2025: The government raised PLI funding for pharmaceuticals from INR 2,150.50 crore to INR 2,444.93 crore to spur drug delivery device manufacturing.
- December 2024: Cipla launched Afrezza, India’s first inhalable insulin, offering needle-free diabetes management.
- April 2024: Sanofi India launched Soliqua, a once-daily fixed-ratio insulin and GLP-1 injectable therapy, after CDSCO approval.
India Drug Delivery Devices Market Report Scope
As per the scope, drug delivery devices are specialized tools for the delivery of a drug or therapeutic agent via a specific route of administration. These devices are used as part of medical treatments. The India Drug Delivery Devices Market is segmented by Route of Administration (Injectable, Topical, Ocular and Others), and Application (Cancer, Cardiovascular, Diabetes, Infectious Diseases, Others). The report offers the value (in USD million) for the above segments.
| By Device Type | Injectable Delivery Devices |
| Inhalation Delivery Devices | |
| Infusion Pumps | |
| Transdermal Patches | |
| Implantable Drug Delivery Systems | |
| Ocular Inserts and Delivery Implants | |
| Nasal & Buccal Delivery Devices | |
| By Route of Administration | Injectable |
| Inhalation | |
| Transdermal | |
| Oral Mucosal (Buccal and Sublingual) | |
| Ocular | |
| Nasal | |
| By Application | Cancer |
| Cardiovascular Diseases | |
| Diabetes | |
| Respiratory and Infectious Diseases | |
| Neurological Disorders | |
| Others | |
| By End User | Hospitals |
| Ambulatory Surgical Centers | |
| Home Healthcare Settings | |
| Clinics and Others |
| Injectable Delivery Devices |
| Inhalation Delivery Devices |
| Infusion Pumps |
| Transdermal Patches |
| Implantable Drug Delivery Systems |
| Ocular Inserts and Delivery Implants |
| Nasal & Buccal Delivery Devices |
| Injectable |
| Inhalation |
| Transdermal |
| Oral Mucosal (Buccal and Sublingual) |
| Ocular |
| Nasal |
| Cancer |
| Cardiovascular Diseases |
| Diabetes |
| Respiratory and Infectious Diseases |
| Neurological Disorders |
| Others |
| Hospitals |
| Ambulatory Surgical Centers |
| Home Healthcare Settings |
| Clinics and Others |
Key Questions Answered in the Report
1. What is the projected size of the India drug delivery devices market by 2030?
The market is forecast to reach USD 11.56 billion by 2030, growing at a 10.93% CAGR.
2. Which device type currently dominates sales in India?
Injectable delivery devices hold a 45.0% revenue share, driven by widespread use in diabetes and biologic therapies.
3. Why is the nasal route gaining traction in drug delivery?
Nasal devices bypass the blood–brain barrier, offer needle-free administration, and are projected to grow at an 11.45% CAGR through 2030.
4. How are government policies shaping domestic manufacturing?
Expanded PLI funding and state-level incentives have attracted INR 1.46 lakh crore in investments, reducing import dependence and supporting local innovation.
5. What restrains wider adoption of implantable drug delivery systems?
High out-of-pocket costs and limited insurance coverage make USD 2,000-5,000 implantables unaffordable for many patients, particularly outside metro markets.
6. Which end-user segment is the fastest growing?
Home healthcare settings are expanding at a 13.67% CAGR as connected devices enable safe self-administration and remote monitoring.



